Are Ferns Pteridophyte
Are ferns pteridophytes? Well, ferns are mostly common greenery foliage plants that neither produce any seeds nor flowers.
equivalently, pteridophytes are also known as seedless vascular plants that germinate via spores. In general, ferns belong to the pteridophyte groups and are severally divided among many species because of their class and diversity.
If you want to know more about this topic, get along with this article from the last. Here I’ll try to give you a classification of pteridophyte groups along with trying to elaborate on what is actual pteridophyte.
Besides, I’ll try to make a connection between ferns and pteridophyte class by showing their anatomy, class, and different varieties in this article. So let’s get started. Ferns species belong to the pteridophyte class from the.
What is Pteridophyte?
A Pteridophyte is a collective phylum or vascular plant which reproduces by spores. These vascular plants are articulated by xylem and phloem tissue.
The xylem transports tissue in vascular plants that transport water and minerals to the root system. On the contrary, Phloem is the living tissue in vascular plants which surplus the soluble organic compounds at the time of photosynthesis.
Ultimately, pteridophyte is a vascular plant that neither produces any seeds nor flowers. Because of their characteristics, they are sometimes referred to as cryptogams (produce spores).
It means they are known for their hidden reproduction.
Anatomy of Phylogeny
In the pteridophyte diversity, ferns have around 90% similarities to this diversity. According to the 2006 classification survey, Tracheophyta is a vascular plant and Lycopodiophyta is the subdivision.
In the Lycopodiophyta groups, there are 1 subclass and 3 orders and each order consists of 5 genera where almost 1300 species are there. Similarly, in the Polypodiophyta groups, there are 4 subclasses.
- Subclass 1: Equisetidae.
- Subclass 2: Ophioglossidae.
- Subclass 3: Marattiidae.
- Subclass 4: Polypodiidae.
These subclasses have 11 orders, 21 families and each consists of 212 genera with 10,535 species.
Groups of Pteridophyte
Now go through some groups and diversity of pteridophyte genera.
Lycopodiophyta
Tracheophyta are primary sources of vascular plants where Lycopodiopsida or Lycopodiophyta is the main class and lycophyte is subdivision in the category.
Lycopodiophyta are described as groups of vascular plants and are also referred to as ferns plants. It’s one of the oldest groups of vascular plants that are 425 million years old and first evolved with pteridophytes.
In this category, clubmosses, quillworts, and spikemosses are the 3 extant orders.
Polypodiophyta
Polypodiophyta or Polypodiopsida are also a group of vascular plants that neither give seeds nor flowers but produce via spores.
More than 10,000 species are there in Polypodiophyta groups which are frequently divided into multiple branches.
However, it again has four classes which are: Equisetidae, Psilotopsida, Marattiidae, and Polypodiaceae.
Equisetidae
Equisetidae is one of the four classes of Polypodiophyta which are also known as horsetails. These plants typically inhabit wet areas with their needle-like branches.
Mostly their branches are in vertical shapes. They are now in the fern category because of their specialized lineage.
Psilotopsida
Psilotopsida is the 2nd subclass of Polypodiophyta or ferns groups. This category of class is commonly referred to as whisk ferns, grape ferns, moonworts, and adder’s tongue ferns.
So, this Psilotopsida class has 2 orders which are whisk ferns and Ophioglossoides ferns consisting of 92 species. Many varieties of these whisk fern species generally produce fronds every year.
Marattiidae
Marattiidae is the 3rd subclass of the Polypodiophyta groups where Marattiiales are the only order in the category. Also, this family consists of 6 genera which revolve around 110 to 150 different species.
Polypodiopsida
Polypodiopsida is the last class of Polypodiophyta groups. This Polypodiopsida is commonly known as leptosporangiate ferns where it has 7 orders with 9000 to 11000 different species.
Almost a third of leptosporangiate species are epiphytes where their sporangia arises from a single epidermal cell instead of groups of cells.
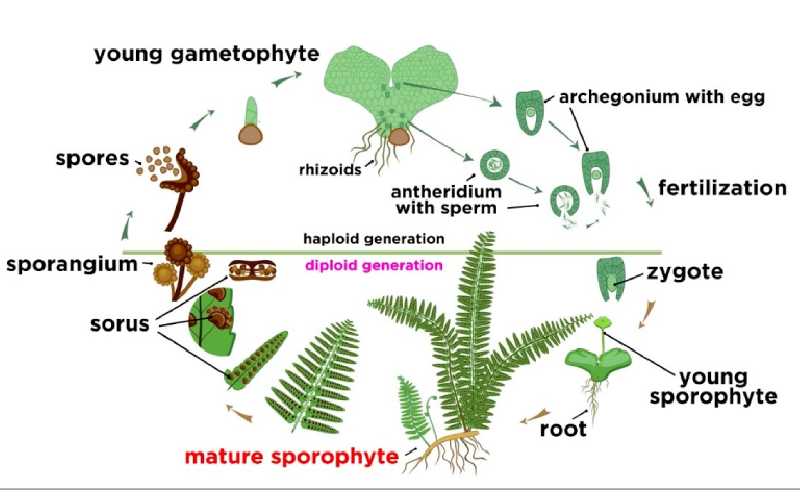
Life Cycle of Pteridophyte
Since Pteridophytes produce spores and germinate from this process; they need to complete two steps of their life cycle which are the sporophyte phase and gametophytes phase. In the first phase of Sporophytes, it actually unleashes the spores.
Sporophyte plants are diploid, meaning 2n chromosomes. In this process, sporophyte produces sporangia underneath the fronds or fertile leaves. These fertile fronds or leaves are known as sporophylls. Since gametophytes release the gamete that’s why it’s known as prothallus as well.
Also, gametophyte plants are haploid; they contain n-chromosomes within themselves. In the gametophyte process, gametes (eggs and sperm) are born or develop from those spores.
Meanwhile, these little gametophytes produce male and female gametes which are called zygotes. Later, the zygote gives birth to another sporophyte and the circle goes on. This is how their life cycle develops from season to season
Why Are Ferns Considered Pteridophyte?
Briefly, all fern species are in the category of Lycopodiophyta and Polypodiophyta class. Along with ferns, horsetail, and lycophytes such as spikemoss, club mosses, and quillworts, all are considered in the Polypodiophyta and Lycopodiophyta groups.
That is why ferns are considered Pteridophytes as they belong in this class. Thus, both Lycopodiophyta and Polypodiophyta classes are a combination of Pteridophyte groups to which ferns belong.
Closing Lines
To conclude, ferns are vascular seedless plants that belong to the pteridophyte groups. Since they neither produce seeds nor flowers, but germinate via spores which is one of the primary characteristics of the Pteridophyte genre.
Similarly, both the Lycopodiophyta and Polypodiophyta classes are a combination of pteridophyte groups where fern species distinguish their individual seedless plant’s characteristics from other seed plants.







